
Insure++ is a unique programming tool designed by ParaSoft company that automatically detects large classes of programming and runtime errors at both compile time and runtime.
It is able to detect a wide variety of typical programming and memory access errors in C/C++ programs, including:
- memory corruption due to reading or writing beyond the valid areas
of global, local, shared and dynamically allocated objects;
- operations on illegal, or unrelated pointers;
- reading uninitialized memory;
- memory leaks ( "memory garbage" that remains unaccessible for the
program after the pointer referring to a memory location has been
stroyed);
- errors allocating and freeing dynamic memory;
- string manipulation errors;
- incompatible variable declarations;
- mismatched argument types of and/or invalid parameters in library
calls;
- and much more...
Preparation
In order to use Insure++ tool
you have first to adjust your .cshrc
file.
Add the command
source /local/config/cshrc.parasoft
in your .cshrc file.
Note: cshrc.parasoft
should
be sourced AFTER cshrc.standard
or
cshrc.gcc
since it redefines some of the libraries. A better option is to do a
source /local/config/cshrc.parasoft
in the command line everytime you run Insure,
instead of including it in your .cshrc
file.
Also note that after you have completed working with Insure, you should
do a
source /local/config/cshrc.gcc
in the command line, to get back all the original gcc libraries.
In case you have done the source cshrc.parasoftin
your .cshrc file,
then
after that do a
source /local/config/cshrc.gcc
to
restore gcc.
How to run the INSURE++ tool
You use Insure++ by processing your program with the special insight program in place of your normal compiler. This creates a version of your code which includes calls to the Insure++ library and then passes it to your normal compiler. Then you run your program in the normal fashion.
During the compilation process Insurewill report a variety of programming errors. For each error reported you will see the source code line that appears to be incorrect and an explanation of what type of error occurred. Insra is a Graphical user interface for displaying error messages generated by Insure++.
Let's start with an example of debugging session.
Copy file bubble1.c to your directory.
Enter the command
insure -g -o bubble1 bubble1.c
Note: If you are running your program from a remote host, then you must set the display environment in the machine that you are currently working in. Type in the following command in the command line before running Insure:
setenv DISPLAY your_machine:0.0
For example, if I run the program in oso, from herbrand, I type the following in the command line:
oso:[9] setenv DISPLAY herbrand:0.0
oso:[10] insure -g -o bubble1 bubble1.c
oso:[10]
This will create an executable file bubble1
with necessary calls to the Insure runtime library. An Insra
window pops up that indicates that there are no compile time errors detected,
as is seen below:

Now you can run you program by typing
bubble1
in the command line, just as you do while compiling with the normal compiler.
The Insra window shows a bug symbol and the message READ_BAD_INDEX as is seen below:
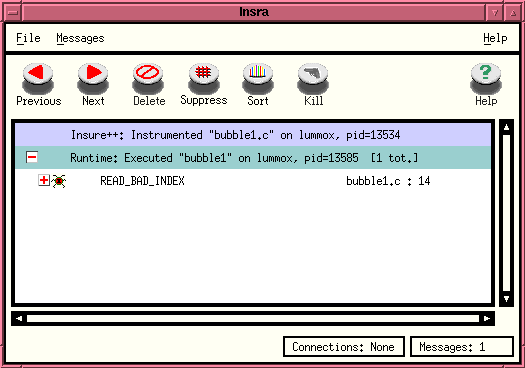
you can click on the '+' icon in the Insra
window to get a detailed explanation of the error.
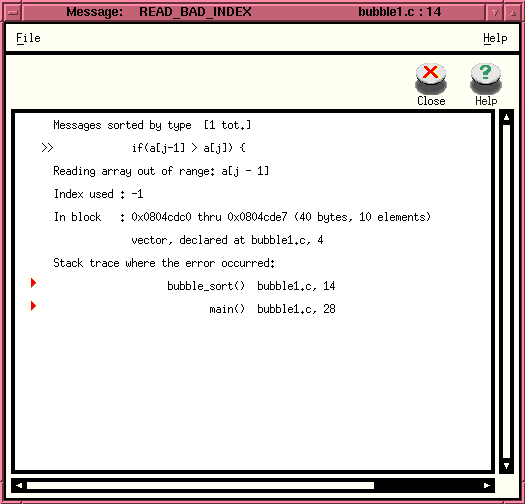
In the example shown, Insure
has detected two runtime errors when the array index is out of range. If
you click on each bug icon
(the red arrow icon) it will open a vi editor window showing
the whole source code file and the line that contains the error:
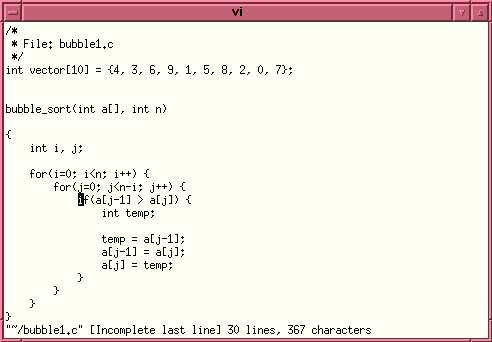
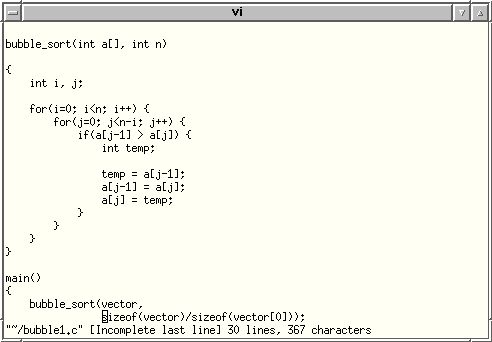
It is possible to edit the source code, if you feel comfortable with the vi editor, or you can open Emacs and to do necessary editing there.
Try more examples that represent some typical C/C++ errors which are
not detected by the compiler:
Home Assignment
(10 points)
Write your own example of a small C program that manipulates an array index. Plant an error in this program and see if Insure++ could detect this bug at the runtime. Submit your example to TA with a brief explanation of the bug planted and the results of your experiment with Insure++.
If you could prove that your program contains a bug (reading/writing beyond the array boundaries) that Insure++ does not detect, you are eligible for a bonus 5 points.
NOTE:
Due to some technical problems the insure++ software is not available
on the Linux machines. So, you are expected to log on to the solaris machines
and do the assignment. The names of the solaris machines onto which you
can login are
guinness, moretti, budvar, ceres, chimay. You can use any one
of these machines.
This can be done using the following procedure,
1. To allow remote machines to open windows on your display, use the following command
oso[1]% xhost budvar
budvar being added to access control list
2. Remote login to one of the solaris machines.
oso[2]% rlogin budvar
Last login: Wed Mar 8 13:36:37 from oso
Sun Microsystems Inc. SunOS 5.7
Generic October 1998
You have new mail.
budvar[1]%
3. You need to instruct the machine(here budvar) to open all windows on your local machine (here oso).
budvar[1]% setenv DISPLAY oso:0.0
4. If you are using a directory other than the home directory for this lab, then change your directory.
budvar[4]% cd cs371
budvar:/home/grad2/ppesara/cs371
5. To use the insure++ tool run the following on your command line.
budvar[5]% source /local/config/cshrc.parasoft
6. Run the sample program using insure.
budvar[6]% insure -g -o bubble1 bubble1.c
** Insure messages will be sent to Insra **
7. Run the executable code "bubble1".
budvar[7]%bubble1
If you have any questions regarding the assignment email me or you can
meet me in my Office Hours.