CS 480 Lec 6 FA22
CS 480 M01 Lecture Notes 6 - Sep 12, 2022
Last Time
Ch 4. Process Control Part 1
Components:
Address space
+ set of data structures within the kernel
Software Architecture of the Linux OS
States: Runnable, Sleeping, Stopped, Zombie
Process Attributes / Parametera: PID, PPID, UID, EUID, GID, EGID, Niceness, Control terminal,..
Life Cycle
Signals: Main Signals, catching, blocking/ignoring
kill CONT ("-bash: kill: CONT: arguments must be process or job IDs" error & process gone) vs. kill -CONT
Ch 4. Process Control Continued
Signals Continued
Signal blocking/ignoring - preventing signal from arriving to the process (some cannot be blocked: KILL, STOP, CONT)
- blocking - signal queued for delivery, delivered after the signal gets unblocked & handler called just once no matter how many times the signal arrived
- ignoring - signal is discarded
sending a signal kill, killall, pkill
Process Monitoring
-
PS Fields
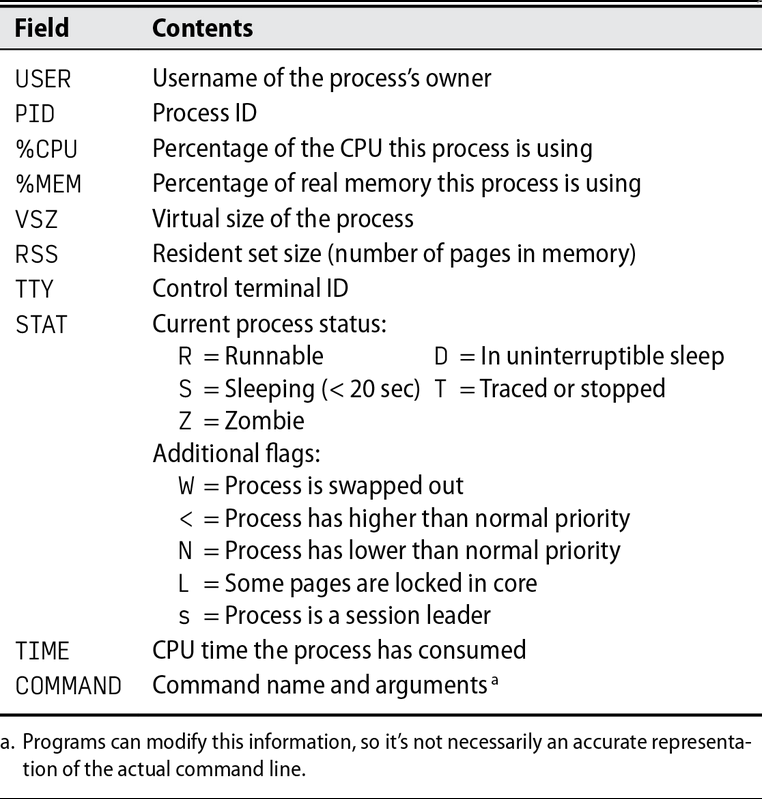
- ps
- ps auxw
- ps alx (more technical info: PPID, NI, WCHAN )
- ps axo stat,euid,ruid,tty,ppid,pid,pcpu,pmem,vsz,rss,args
- top
The /proc Filesystem
Pseudo filesystem with kernel info about the system:
cmdline, environ, exe, stat, statm, ...
Read by ps and top
strace
Observe every system call the process makes and every signal it receives.
Runaway Processes
- consume significant CPU/network/disk resources (bugs or inefficient programs)
- user's
- system - shouldn't happen ! ( ? resource hog)
- identifying ... hw assignment ...
-
Runaway processes may fill up filesystem ... df, du, fuser, lsof
Periodic Processes
Many tasks need to be done repeatedly and ... ideally without human intervention
Automate ! shell, perl, python, ... + execution without human interventation => consistency & reliability
cron - tool to run commands on a predetermined schedule
- daemon (started at boot time)
- config file(s): crontab(s) - commands executed by sh (does not act as login shell -> env vars ...)
==> can do almost anything we can do from the command line
per user too !
one configuration file per user - located in
/var/spool/cron
| /tabs | Suse |
| /crontabs | Slackware, Debian, UNIX, .. |
/var/cron/tabs FreeBSD
Linux Vixie-cron extensions that allow a command to run as any user (extra username field infront of the command)
/etc/crontab - intended for sysadmins to maintain by hand
/etc/cron.d - intended for software packages
Linux distros also have directories to run scripts from: /etc/cron.hourly ,
/etc/cron.daily ,
/etc/cron.weekly ... hw assignment ...
format of crontab
comments - start with #
minute hour day month weekday [username] command
( executed by /bin/sh by default - can be changed through SHELL variable)
* - matches everything
plus stepping (/), ranges ( -), list (,)
- as a first character of an entry ???
* * * * * echo "aaaa ... " >> /tmp/log
0-29,45-59/3 * * * * echo "bbbb ... " >> /tmp/log
*/2 * * * * (date; echo "2222 ... " ) >> /tmp/log
20 3 1 * * rotate.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
plus examples in book ...
0,30 * 13 * 5 ???
The day needs to satisfy only one of the two conditions in order to be selected.
PATH=/bin:/usr/bin
* * * * * echo $(date) - $(uptime) >> ~/uptime.log
Check email for errors!
crontab command notifies the daemon about changes
- replaces the previous version of the table / schedule
- -e
- -l
- -r
- ^D v. ^C (non Linux problem mostly - erase vs escape)
/etc/cron.deny
/etc/cron.allow
Acces control implemented by crontab not cron... !
Systemd timers ...
common uses - p. 288
simple reminders
cleaninng file systems (/tmp, /var/tmp)
distribution of config files over network
rotating log files

