CS 480 Lec 1 FA22
CS 480 M01 Lecture Notes 1 - Aug 22, 2022
Chapter 1. Where to Start
Administrator's tasks
- Controlling access / Account provisioning / User management - creating, removing, password resetting, ...
- HW maintenance - adding / replacing parts, buying new computers, ...+ virtualization
- Automating tasks - efficiency, fewer errors, fast response to changing requirements, ... BUT chance to mess up more !
writing programs / scripts may require analytical and architectural skills...
- Backups - "perhaps the most important job" - daily usually
- Software installations and maintenance - under several OS / HW platforms + upgrades and updates
- System monitoring - make sure that basic & most important services work ( login, NFS, mail, web, disk space, .), don't expect much feedback from users
- Troubleshooting - systems do fail; finding the problem is often harder then fixing it
- Local documentation - both for users and sysadmins
- Security - security policy, monitoring, patching, ...
- Tuning performance
- Developing site policies
- Working with vendors
- Fire fighting & Helpdesk (perception to users of what's important)
- Network maintenance / upgrading
- User education
- Special requests
- Long term planning / design / budget
- Inventory
Suggested Background
- user level experience with linux or unix
- editors: vi (vim, vimtutor), pico, emacs, ..., gedit (GUI), ... NOT:
MS word, notepad,...
- programming / scripting: sh (csh, tcsh, bash), Perl or Python or Ruby plus expect (front end driving interactive programs) , and sometimes even C ...
Linux/Unix relationship
Linux is a reimplementation and elaboration on the UNIX kernel.
Conforms to POSIX standard and is compatible with most existing UNIX software.
Free, open source, cooperatively developed
- Linux 1991 Linus Torvalds -> 1994 kernel v. 1.0 (A.S. Tanenbaum's Minix offshot)
- Unix
- 1969 AT&T Labs (Thompson, Richie, Kernighan, ..)
- 1976 - free to universities -> BSD in 1977 for PDP-11
.... -> BSD 4.4 in 1993
.... -> 4.4BSD-Lite -> NetBSD, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, user space of Mac OS X, ...
- UNIX: AT&T -> UNIX System Labs. sold to Novell in 1993 -> SCO in ??
Dec 1991 System V Release 4
-> most commercial versions today are based on that (Solaris, AIX, HP-UX, IRIX,..)
- Linux - latest stable kernel version : 4.X.Y
defines the kernel only
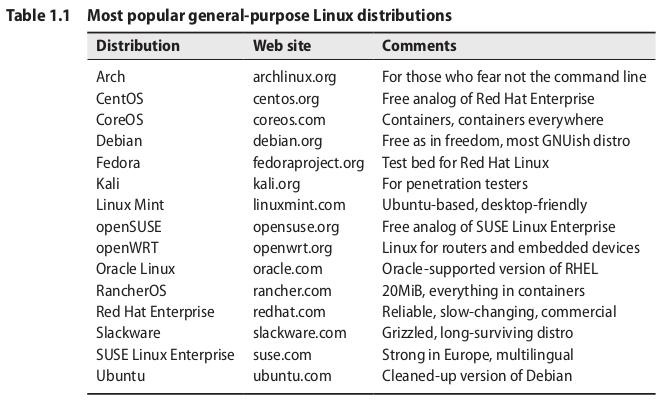
Distributions:
"A linux distribution comprises the Linux kernel, which is the core of the operating
system, and packages that make up all the commands you can run on the system."
- share the same kernel lineage
- not that much different but they do differ in
- focus
- extra sw packaged with the distribution (latest /stable / tested ?)
- file system layout ...
- support (online docs, discussions, real people to talk to, security patches available fast, ....)
- admin tools
- ...
- questions to ask are when choosing distro:
- Is it going to be around in five years?
- Is it going to stay on top of the latest security patches?
- Does it have an active community and sufficient documentation?
- If I have problems, will the vendor talk to me, and how much will that cost?
- ...
- Is it going to update software packages often enough / stay on top of the latest development?
- How often does the particular version become obsolete / how often and when am I forced to uprade ?
-
Linux Distribution Timeline
copied from (Linux Distribution Guide at LinuxLinks.com ...)
newer version on wikimedia
-
Online lists of distributions:
next ... Units, Where To Go For Info, Chapter 3: Access Control and Rootly Powers
