- ...
categories1
-
Natural categories are those for which people can readily associate
typical members. For instance, CHAIR would be a natural
category instead of FURNITURE. Natural categories are also
referred to as basic-level categories, because they tend to occur at
the level in a taxonomy where most of information resides, in terms of
attributes [103,102].
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
languages.2
-
The EuroWordNet project [119] is seeking to tie
together separate ``wordnets'' that are being developed for several
different languages. It is addressing the problem of having separate
ontologies for each language by specifying high-level
correspondences.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... test:3
-
The
likelihood is generally defined as the conditional probability of the
data (or evidence) given the hypothesis, which would be
 for the verb case. Via Bayes's Theorem, this can be
rewritten
for the verb case. Via Bayes's Theorem, this can be
rewritten
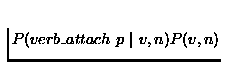 and, since the prior
probabilities cancel in the likelihood ratio, the form given above
results. Logarithms are often used with likelihoods ratios (hence the
log-likelihood test) to make combinations additive rather than
multiplicative[85].
and, since the prior
probabilities cancel in the likelihood ratio, the form given above
results. Logarithms are often used with likelihoods ratios (hence the
log-likelihood test) to make combinations additive rather than
multiplicative[85].
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... text4
- This co-occurrence matrix reduction algorithm is
similar to that used in latent semantic analysis
[33,42], which is not discussed in this
review.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
alternation.5
-
The dative alternation licenses ``X give Y to Z''
 ``X give Z Y'.
``X give Z Y'.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
expressions6
- This uses the following conventions: X matches
category X; . matches any category; X* matches 0 or more X's;
X? matches 0 or 1 X's; and,
 applies rule Z
applies rule Z
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... parser7
-
The Microsoft English Grammar (MEG) parser is based on the PLNLP
English Grammar (PEG) parser developed at IBM (PLNLP stands for
Programming Language for NLP).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... function8
-
Zipf's law states that a term's frequency is inversely proportional to
its rank (e.g., frequency of third most common term is one-third that
of the first). The curve plotting this relationship can be viewed as
the top half of a hyperbola (rotated 45 degrees).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
 for the verb case. Via Bayes's Theorem, this can be
rewritten
for the verb case. Via Bayes's Theorem, this can be
rewritten
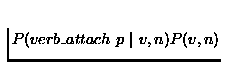 and, since the prior
probabilities cancel in the likelihood ratio, the form given above
results. Logarithms are often used with likelihoods ratios (hence the
log-likelihood test) to make combinations additive rather than
multiplicative[85].
and, since the prior
probabilities cancel in the likelihood ratio, the form given above
results. Logarithms are often used with likelihoods ratios (hence the
log-likelihood test) to make combinations additive rather than
multiplicative[85].
 ``X give Z Y'.
``X give Z Y'.
 applies rule Z
applies rule Z